Today’s customer journey through your company website, web pages and marketplace sales platforms often meanders across multiple websites, social media sites, links to authoritative websites, company-review platforms and paid advertising including media ads, content marketing and PPC campaigns. It’s critical to know which campaigns are delivering the highest returns in sales, leads and achieving other company goals. Attribution modeling is the process of choosing how to credit various promotional efforts that result in conversions.
Measuring how well your marketing campaigns are doing isn’t always an exact science because there are so many variables that influence customer decisions. Some customers buy because they enjoy the convenience and responsiveness of a company’s website. Others buy because they read a favorable review. Many site visitors buy because of the convincing content they find on a given website.
What Is Attribution Modeling?
There are many attribution models because of the many types of marketing campaigns. Most companies run multiple campaigns, so your sales and lead conversions might depend on multiple touch-points along the customer’s digital journey. Attribution modeling is the set of rules that you implement to credit different promotional efforts for leads, sales and other types of conversions. These conversions might include getting customers to fill out a survey, make a reservation, opt-in to receive newsletter or request further information.
Why Is Your Attribution Modeling Approach Important?
Without attribution modeling, it would be difficult or impossible to estimate how well your marketing campaigns are performing. Most Internet marketers use a combination of display ads, content marketing, pay-per-click, or PPC, campaigns and other organic-search, (SEO) marketing. Attribution modeling assigns credit for a sale or other type of conversion based on various formulas, or algorithms.
Marketers can use these data points to analyze customer behavior and find out which marketing initiatives deliver the highest conversion rates, greatest profit and other key benchmarks. Poorly performing campaigns can be adjusted or abandoned, and successful ones can be expanded. You can analyze both onsite and offsite customer behavior and assign credit accordingly. Attribution models generally work in three technical ways when analyzing offsite marketing initiatives:
MCA-O2S Protocol
- MCA-O2S Protocol This coding protocol attributes the offline impact of various promotional efforts that don’t involve the Internet.
MCA-AMS Protocol
- MCA-AMS Protocol This method awards credit for multiple campaigns and promotional efforts across multiple devices such as phones, televisions, laptops and computers.
MCA-ADC
- MCA-ADC This protocol assigns credit for all digital channels including social media, display advertising, links, PPC campaigns, etc.
Various Approaches for Attribution Modeling
There are many attribution models that cover different scenarios and strategies for portioning credit, and many custom solutions that use proprietary attribution models with unique combinations. These recommendations can help to determine your attribution strategy:
- Map the customer’s journey and include all channels, touch-points, links, PPC campaigns and interactions such as customer service contacts.
- Carefully consider lead quality and how often leads turn into conversions.
- It’s important to consider your campaign objectives and whether you are looking for short- or long-term results.
- Test, monitor and adjust your campaigns and attribution strategies as needed to maximize results.
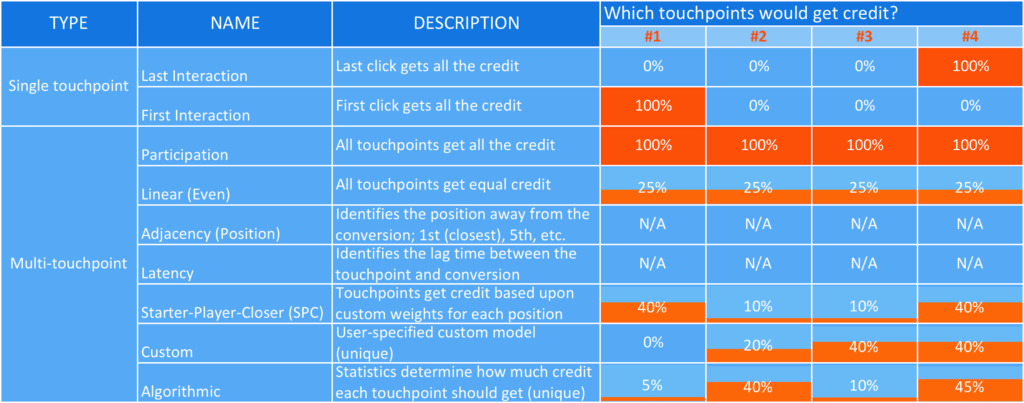
Source: blogs.adobe.com
No single attribution model works perfectly for every business or marketing strategy. That’s why it’s important to know your short-and long-term goals and choose the method that delivers the best progress toward those goals. The following approaches for attribution modeling assign credit in various ways according to a Google AdWords attribution tutorial and an article posted at Impactradius.com:
Last-Click Model
- Last-Click Model Last click attribution credits success to a customer’s last click. The theory is that the last thing a customer does before buying is the most influential. This method works well in short sales cycles, when offering incentives and organizing email campaigns. Last click is the most popular attribution model, but the method isn’t very effective for long sales cycles or when using multi-channel or alternative marketing strategies.
First-Click Model
- First-Click Model First click attribution works well for companies that are trying to build their brands and only advertise on a couple of channels. This method is effective when customers have limited ways to find your business. This makes it easier to gauge brand awareness and find out which channels are most effective for attracting new customers.
Last Non-Direct Click
- Last Non-Direct Click Direct traffic is ignored in this attribution model, and all credit is assigned to the last non-direct click. For example, a customer sees a display ad for your company on another website and clicks on it. Three days later, the customer navigates directly to your site and buys the product. The display ad is credited for the sale.
Position-Based Attribution
- Position-Based Attribution This is a complex method of awarding credit that most heavily attributes credit to the first contact but also awards some credit to the last click. This model also recognizes the contributions of any channels between the two events that help to nurture the sale.
Time-Decay Model
- Time-Decay Model Some companies choose to assign greater credit for faster conversions. The faster the conversion, the greater the amount of credit that will be assigned to the connection. Delayed sales are rewarded with diminishing credit.
Even-Attribution Model
- Even-Attribution Model This model gives equal credit to every touch-point on the customer’s journey. This method works well for B2B companies and products that are heavily researched.
Position-Based Model
- Position-Based Model Companies that value referrals from associates and influencers often use this model because it rewards introducers and closers equally.
Algorithmic, or Data-Driven, Model
- Algorithmic, or Data-Driven, Model This model can be adjusted based on various external conditions. The method uses data-driven insights from online and offline marketing channels across all types of devices to assign credit. The method assigns credit based on how people search for a business and what factors persuade them to become customers. This attribution model is popular with companies that use nontraditional marketing and unusual channels to drive sales conversions. In some ways, this method mirrors the algorithmic formulas that Google uses to rank websites in search engine return pages.
Using Analytics to Increase Conversion Rates
The important thing about attribution modeling is that it allows you to determine how well your marketing efforts are doing. The method that you choose can depend on many factors such as whether you only use organic marketing, PPC advertising, social media promotions or combinations. It’s also possible to use different attribution models for different marketing initiatives and marketing platforms such as social media pages, website clicks, Google AdWords campaigns, marketplace platform sales (such as eBay and Amazon) and other promotional efforts.
The critical issue is measuring and monitoring your return on investment, or ROI. Without strategic analysis, you could be wasting money on unproductive paid campaigns while your sales are coming from PPC advertising. Your social media promotions might be generating a solid return while you organic SEO marketing just isn’t working. A Salesforce report on conversion rates found that it takes between 6 to 8 clicks to generate a qualified sales lead and that up to 60 percent of the buying decision is already made before a customer talks to a salesperson or staff member. That’s why choosing the most favorable and cost-value approach depends on carefully studying which attribution model delivers the greatest return for the investment in time, money and your company’s reputation.
Helen Cartwright is a freelance blogger

